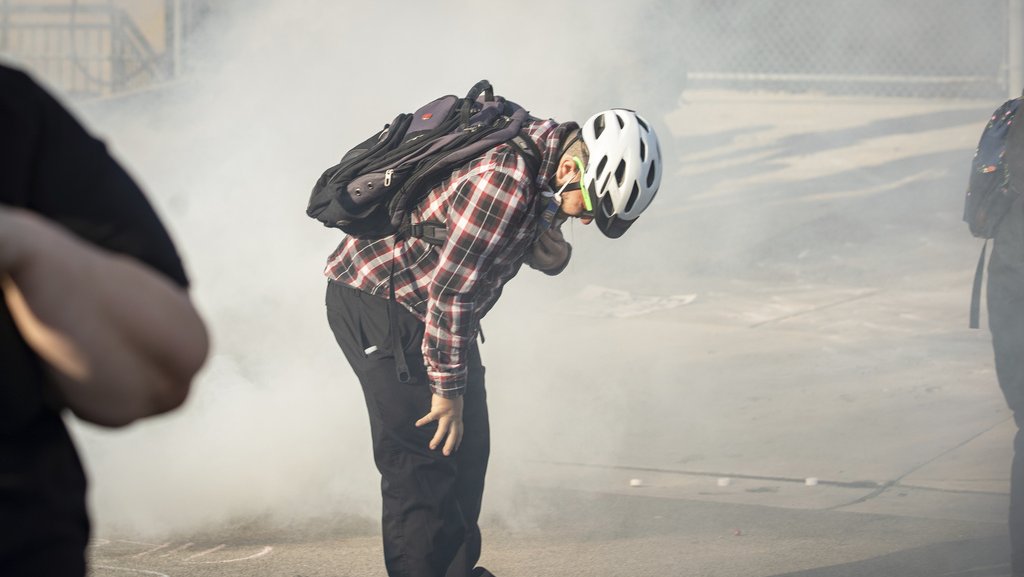
A federal judge just reminded the government that the First Amendment still applies in Chicago.
On Oct. 9, Chicago journalists and protesters scored a major legal win, when Judge Sara Ellis issued a temporary restraining order reigning in federal officers’ repeated First Amendment violations at protests.
It’s a big victory for press freedom. The order prohibits arrests and use of physical force against journalists and restricts the use of dangerous crowd-control munitions. It defines “journalists” broadly, in a way that includes independent, freelance, and student reporters. It also enhances transparency by requiring federal officers to wear “visible identification,” like a unique serial number.
This order and similar rulings in Los Angeles last month are powerful reminders that journalists working together can vindicate their rights in the courts. They also highlight the crucial role that independent journalists and smaller news organizations play in defending press freedom. In both Chicago and Los Angeles, it’s been freelancers, community news outlets, local press clubs, and unions who’ve taken the lead, teaming up with protesters, legal observers, and clergy to take the government to court.
Unconstitutional dispersals of press still possible
But the fight isn’t over. The Chicago order unfortunately leaves open the possibility that, at least in some instances, federal officers may order journalists to leave areas where protests are being broken up or officers are attacking protesters.
Although the order prohibits dispersal of journalists from protests as a general matter, it also states that officers can “order” journalists to “change location to avoid disrupting law enforcement,” as long as they have “an objectively reasonable time to comply and an objectively reasonable opportunity to report and observe.” (In contrast, a similar order in Los Angeles states only that federal officers may “ask” journalists to change location.)
Federal officers are likely to use this as a loophole to continue to violently remove the press from protests, on the pretext that it’s necessary to avoid disruption. The order’s requirement that press must be able to continue to report and observe is also too lax; far better would have been an order specifically requiring that press be able to continue to see and hear the protest and law enforcement response.
Even when police can disperse protesters who break the law, the First Amendment doesn’t allow them to disperse journalists, too.
The weaker language around dispersals of journalists in the court’s order is a shame, especially for the public’s right to know. In recent days, Chicago journalists have been reporting about the violent tactics used by federal agents to disperse protests. If journalists can be ordered to leave alongside protesters, they can’t observe what’s happening or capture the images they need to keep the public informed.
It also makes dispersals more dangerous for protesters. As Unraveled Press noted, “Again and again, we’ve seen cops are most likely to get more violent with demonstrators when out of public view.” (Unraveled Press co-founder Raven Geary is a plaintiff in the Chicago lawsuit.) And while the court’s order prohibits dispersal orders aimed at peaceful protesters, if federal officers violate that order and also disperse the press to avoid a “disruption,” it will be much harder for the public to learn about it.
By declining to simply prohibit federal officers from dispersing the press, except when necessary to serve an essential government need such as public safety, the court also got the law wrong. Even when police can disperse protesters who break the law, the First Amendment doesn’t allow them to disperse journalists, too.
We’re not the only ones who say so. Just last year, the Department of Justice issued guidance stating as much:
“In the case of mass demonstrations, there may be situations—such as dispersal orders or curfews—where the police may reasonably limit public access. In these circumstances, to ensure that these limitations are narrowly tailored, the police may need to exempt reporters from these restrictions. …”
The DOJ also said so in a previous report, reprimanding the Minneapolis Police Department for its suppression of protesters and the press following George Floyd’s murder:
“The First Amendment requires that any restrictions on when, where, and how reporters gather information ‘leave open ample alternative channels’ for gathering the news. Blanket enforcement of dispersal orders and curfews against press violates this principle because they foreclose the press from reporting about what happens after the dispersal or curfew is issued, including how police enforce those orders.”
And in an important decision from 2020, the federal court of appeals in the 9th Circuit also disapproved of blanket dispersal orders being enforced against the press. That case arose from very similar circumstances to those today: federal authorities abusing the First Amendment while policing federal property during Black Lives Matter protests in Portland, Oregon.
In the 2020 case, the 9th Circuit affirmed a legal order that exempted journalists from general dispersal orders issued by the federal government. Journalists, it wrote, “cannot be punished for the violent acts of others.”
These authorities make it clear: Journalists cannot be ordered to move simply because it would be more convenient for officers. Journalists can only be dispersed if it’s essential to a compelling government interest, and only if they continue to have another vantage point from which they can see and hear what’s going on in order to report.
It’s frustrating that the court’s order leaves the door open for the government to evade this well-established principle. But the fight isn’t over. The court’s temporary restraining order is just a first step. When it issues a more permanent ruling, it will have another opportunity to get the prohibition on dispersing the press right.