Also available in Spanish.
Passwords are the brittle wall that keeps unwanted visitors out of your accounts. When it comes to account protection, two-factor authentication is one of the most effective defenses available.
Two-factor authentication, or 2FA for short, strengthens login security by requiring a second piece of information — a second factor beyond your password. The second piece of information is usually a temporary code delivered by a device in your possession, such as your phone. It may also be something on your body, such as a fingerprint.
You might hear it referred to by a variety of names, like multifactor authentication or two-step verification, but for consistency, we’re using 2FA throughout this guide.
Why you should use 2FA
When large-scale password breaches happen — and they happen a lot — credentials are often sold and swapped in online marketplaces and hacking forums. Some attackers break into accounts for entertainment, and some, for a payday. It’s typically not personal. In rare circumstances, attackers have a specific group or person in their crosshairs.
Email accounts generally give attackers the most value. Why? You use your email to recover other web accounts.
Ways your account is most likely to get hijacked include:
- Attackers will guess short or predictable passwords.
- After a large-scale password breach, some attackers will use automated scripts to try logging in to multiple websites with the same hacked credentials, just in case you reuse passwords on multiple accounts.
- Attackers will craft fake phishing pages to trick you into divulging your credentials. They’ll usually send an email that seems to come from a trusted source (e.g., Instagram), directing you to an ordinary-looking login page, but the site is a bogus one under their control. This is why it’s important to look closely at the sender field, as well as the URL for the login page. You can learn more about phishing here.
- Spear phishing is targeted phishing. Typically the attacker will do their homework, gathering publicly available information (e.g., social media, public records) to create a good pretext for the phishing email. They may impersonate a friend or colleague and direct you to a forged login page. This is how The Washington Post’s website got hijacked in 2013.
These are common attacks that affect all email services. Enable 2FA everywhere you can, but especially on your email. Check 2fa.directory to see if your favorite service supports it, and if it doesn’t, consider prodding the organization.
2FA approaches
There are a few simple, widely supported approaches for adding 2FA to your accounts. There’s not one “right” way to use it, and each has distinct considerations for security and convenience.
A pretty good option: SMS text messages
Most services allow you to use regular old text messages as your 2FA. When logging in to a site you need a password for, you’ll receive a short confirmation code on your mobile device. Enter the code when prompted during login.
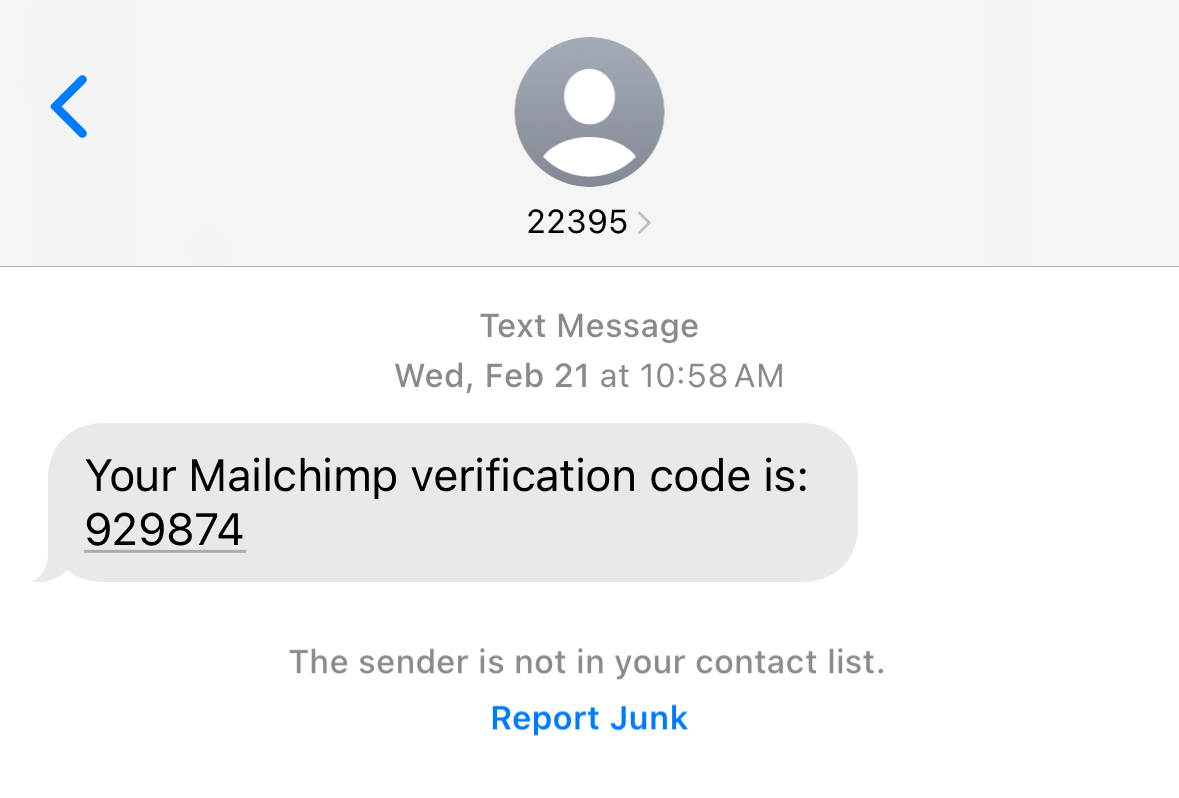
Text messages are a painless way to access 2FA codes, but are only as reliable as the phone network. For example, if you lose network access or travel outside the country, you might not be able to receive the messages.Text messages are a painless way to access 2FA codes, but are only as reliable as the phone network. For example, if you lose network access or travel outside the country, you might not be able to receive the messages.
For most people, SMS-based 2FA is much better than using a password alone. But because telephone infrastructure itself comes with a great deal of baggage, SMS isn’t the most secure method available.
For example, Associated Press writer Fatima Hussein told the story of how someone stole her phone number so they could take over her bank account for financial fraud. The attacker convinced her phone provider, Cricket Wireless, to transfer her number to a new SIM card on a remote device, allowing the attacker to intercept her 2FA messages.
That sounds scary, but remember the real story here: The attacker was forced to work much harder than if they could simply have entered a password.
Better option: Authentication apps
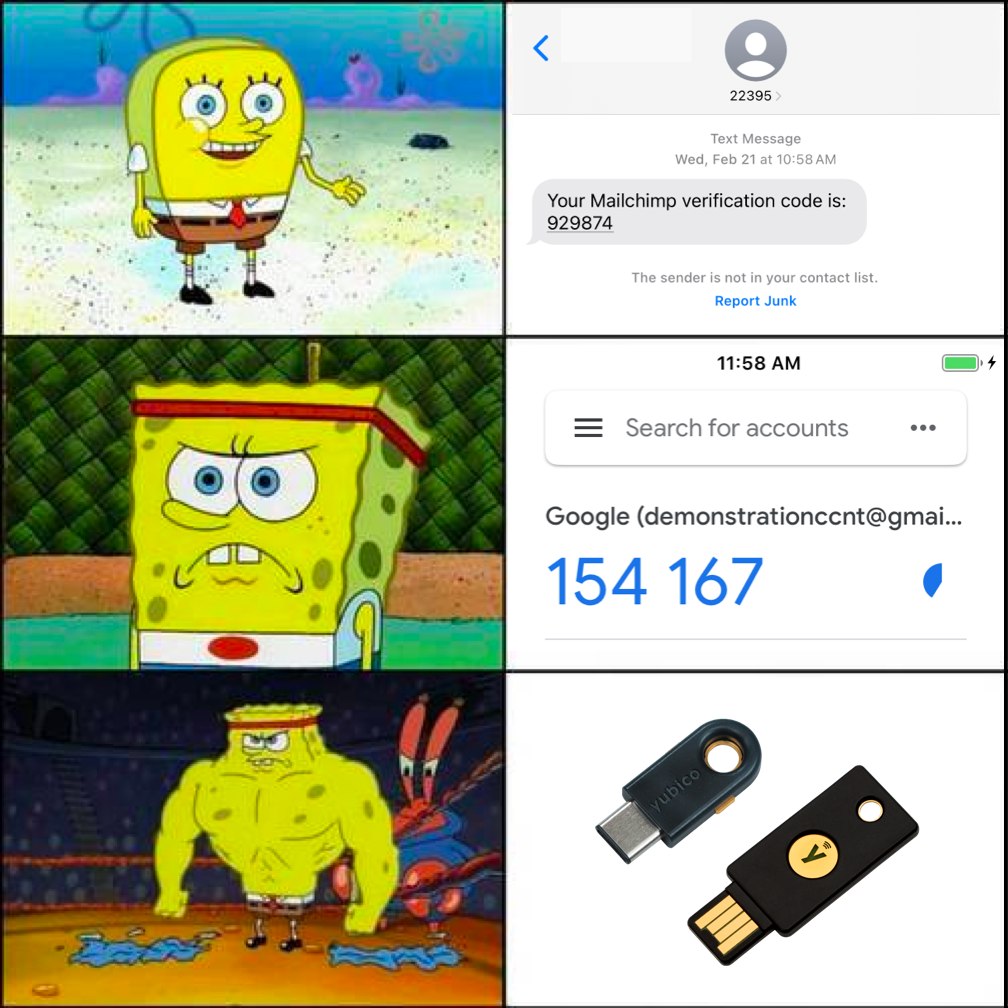
Compared to SMS messages, authenticator apps are a little more convenient and a lot more secure. Some services allow you to receive your temporary login code from a mobile app. There are many options to choose from, such as Google Authenticator or Authy.
Some web services let you attach multiple authentication apps to the same account, which can be incredibly helpful for getting login codes when multiple people need access. Authenticator apps are also great because they work when you don’t have access to your phone network.
Unlike SMS messages, authenticator apps can’t be intercepted on the phone network, making apps a hardened option.
But, just as you can be phished into entering passwords into a fraudulent website to steal your login information, the same is true of authenticator codes. So we can do even better.
Best option: Security keys
Right now, security keys are one of the most secure and efficient ways to use 2FA. A security key is a physical USB device you can use to authenticate into your account.
One of the most popular options, a YubiKey, will run you $25.
Instead of typing in a code when prompted to provide your 2FA credentials, you insert your security key into your device and physically tap it when prompted during login. That’s all. Security keys are fairly resistant to phishing attacks, making them one of the best options available. Unlike code-based 2FA, phishing sites don’t have a great way to intercept information from security keys.
The main problem with security keys is that as soon as you try one, you’ll want to use them everywhere. And they can’t be used everywhere yet.
Security keys are not yet as well supported as authenticator apps, but the standard is getting traction on large websites. It can be used to log into Google, Facebook, Dropbox, and other services. Security keys are supported by most major browsers.
So just to recap, here are our three options:
Use whichever 2FA method is available and practical for you. SMS-based 2FA is a worthwhile upgrade, but when possible, consider using authentication apps or security keys.
Let’s turn on 2FA
You can set up 2FA in minutes. For example, let’s look at how to set it up for Gmail.
First, find the setup page.
Account icon (top right) > Manage your Google Account > Security > Signing in to Google > 2-Step Verification > Get started
First, you must register the device. Punch in your phone number. You’ll be sent a confirmation code on your mobile device, which you will enter on the registration page. If you prefer not to use your phone number, you can always remove it later.
After registering your device, you can use 2FA codes through SMS text messages.
Authenticator app
For a more secure way to use 2FA, activate the authenticator app.
First, go to the application marketplace of your choice and download an authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator, Authy or Duo Mobile.
On the two-step verification page, scroll down to “Authenticator app” and click “Set up.” To register a new service in the app, you will be asked to scan a barcode that appears on your screen. Scan the barcode with your phone’s camera. After the code appears in your app, type the code into the setup prompt.
Once you have an authenticator app, there’s no need to use SMS text messages anymore.
Security keys
Once you’ve purchased your security key, such as a YubiKey, they’re easy to set up.
On the 2-step verification page, scroll down to “Security keys” and click “Add security key.” When prompted, insert the key into the USB port and physically tap it.
Afterward, you can name your newly registered key. Now at login, you’ll just insert and tap the key instead of typing in a 2FA code.
Some laptops (like many MacBooks 2016, and beyond) only have USB Type-C ports. Security keys still work, but you’ll need a USB Type-C adapter. Here’s a short list of Type-C adapters that are confirmed to work. It’s a little more expensive to purchase Type-C YubiKeys.
Tidy up and get started
Once you have authenticator apps or security keys set up, you probably don’t need SMS anymore. Consider removing your phone number.
Scroll to “Voice or text message” and click the pencil icon, then click “Remove phone.”
Finally, even if we lose our security key and authenticator app, we can still avoid locking ourselves out by using backup codes. Scroll down to “Backup codes” and click “set up.”
You will see a series of numeric codes. Print these out and keep them someplace where you can physically access them. If you are ever locked out of your account, you will need one of these codes to get back in.
Don’t stop here. After turning on 2FA, make your accounts safer with strong password habits. Read our guide on how to protect your accounts by using a password manager.



